Generative AI vs. Traditional AI: Choosing the Right Engine for Your Digital Products
In today’s AI-powered transformation, understanding when to employ Traditional AI or Generative AI can set a brand apart. Both carry strengths and trade-offs, especially within the focused contexts of logistics, smart manufacturing, and healthcare. This post will unpack these paradigms through structured paragraphs, data-rich analysis, and actionable takeaways.
1. Defining the Contenders
AI isn’t one-size-fits-all. On one hand:
- Traditional AI excels at pattern recognition, forecasting, and classification. Think supply-chain route planners, predictive machine maintenance, and early cancer detectors.
- Generative AI (GenAI) is all about creation—text, images, code, and even entire simulation scenarios. This model shines when you need fluid, creative output.
Each plays to specific strengths—Traditional AI for precision, Generative AI for creativity, and user-facing intelligence.
2. Logistics: Speed, Sustainability, and Smarter Stories
Traditional AI: The Optimization Backbone
Traditional AI algorithms dominate logistics—optimizing fleet usage, predicting disruptions, and enabling real-time inventory control. According to WifiTalents, AI-driven route planning cuts delivery times by up to 30%, reduces fuel usage by 12–15%, and minimizes maintenance costs by 20%.
Moreover, Business Insider reported that Uber Freight reduced “empty mile” rates from 35% fleet-wide to just 10–15% using route-optimization machine learning.
Generative AI: Human-Centric Context & Scenario Design
GenAI supercharges logistics with empathy and anticipation:
- It crafts personalized customer alerts based on behavior and preferences.
- It designs “what-if” shipping scenarios to balance speed, cost, and carbon footprint.
- It flips reactive firefighting into proactive service.
For example, DocShipper’s GenAI platform reduced transit times by 22% and cut freight expenses by 15% in daily operations.
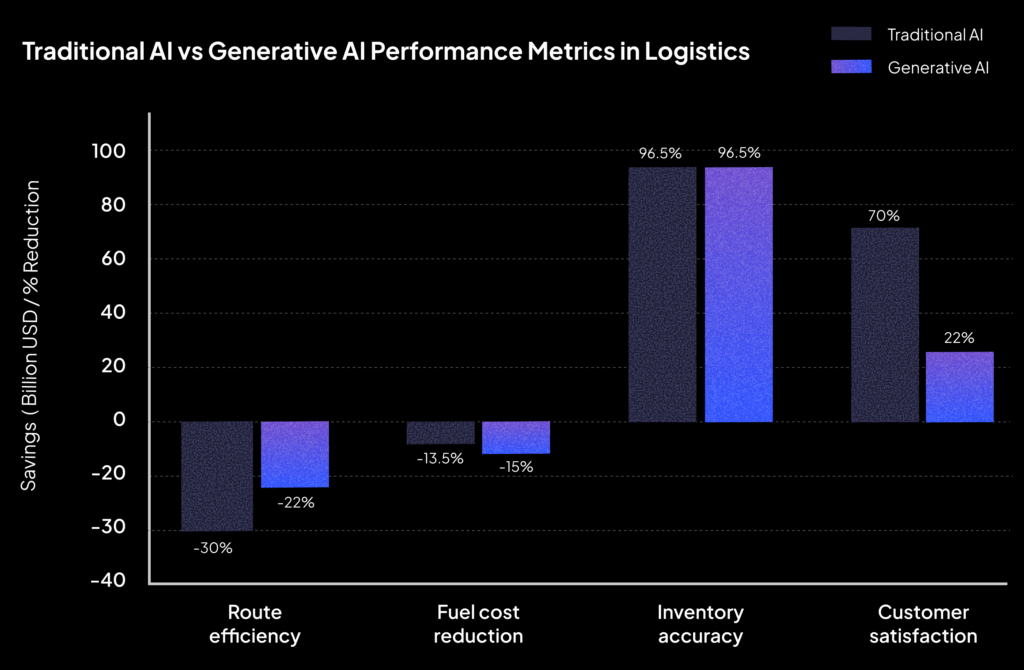
Sources: Global Market Insights, WifiTalents
3. Smart Manufacturing: Precision Meets Creativity
Traditional AI: Reliable Predictors
In smart factories, Traditional AI is the gold standard for:
- Predictive maintenance—cutting downtime and funneling wear signals from equipment into scheduled repairs.
- Quality control—identifying defects via sensor data and computer vision.
- Inventory forecasting and energy optimization.
Business Insider notes companies spend up to $1.4 trillion annually on unplanned downtime—AI-driven predictive maintenance helps eliminate much of that. IoT-integrated systems show 18% energy savings, 22% lower downtime, and 15% better resource use.
Generative AI: Design, Simulation & Adaptability
GenAI is rewriting the manufacturing playbook. Platforms like Autodesk Fusion 360 generate multiple design alternatives (e.g., bicycle frames nearly 25% lighter), while NVIDIA’s Omniverse enables simulation of production-line layout changes for throughput boosts near 18%.
Emerging research dubbed “Industry 6.0” shows GenAI plus robot swarms can deliver product blueprints in 0.5 minutes—47× faster than humans—and complete whole production in just 119 minutes—4.4× faster than expert engineers.
Survey insights from Deloitte reveal 29% of smart-factory leaders have implemented Traditional AI, and 24% are running Generative AI pilots.
4. Healthcare: Diagnosis, Documentation & Drug Discovery
Traditional AI: Accuracy & Efficiency
Traditional AI is already deeply integrated in healthcare
- Diagnostic algorithms with ~70–72% accuracy detect patterns in EHR and imaging data.
- AI diagnostics for mammograms now rival specialist performance.
- Pathology tools are projected to save $12 million over 5 years.
Hospitals see fewer diagnostic errors and more reliable workflows as AI handles scheduling, readmission prediction, and allocation of resources.
Generative AI: Assistants, Summaries & Molecule Innovators
Generative AI goes beyond diagnosis by:
- Drafting patient reports and summarizing histories.
- Powering chatbots that support mental health, triage, and telehealth.
- Designing new drug molecules via deep-learning models.
By 2026, AI is predicted to save $150 billion per year in healthcare in diagnostics and administration, reduce hospital stays by 17.9%, and slash burnout by 54%, per ZipDo data. And while the rise of remote monitoring dropped heart-failure readmissions by ~45%, GenAI-enabled systems continue such a trendsetting.
5. When to Apply Each AI Type
Precision Tasks → Traditional AI
These work best with Traditional AI:
- Route planning, inventory control, and demand forecasting.
- Predictive maintenance and defect detection.
- Medical diagnostics and pattern recognition.
They deliver explainability, trust, and strong ROI on forecasting and optimization.
Creative & Conversational Use Cases → GenAI
Use Generative AI when digital products require:
- Dynamic content (e.g., product descriptions, marketing copy).
- Scenario prototyping and design alternatives.
- Chatbots, assistants, and report generation.
- Drug-molecule suggestions and R&D support.
Blended Solutions → Hybrid Approach
The sweet spot? Layer a GenAI interface over a Traditional AI engine:
- Use Traditional AI as the decision matrix; GenAI handles customer interaction.
- In manufacturing, embed GenAI for scenario planning, with Traditional AI on the factory floor.
- For healthcare, combine predictive models with GenAI-led patient and clinician communication.
6. ROI: The Big Numbers
- A McKinsey study finds 85% of GenAI pilots drive ROI within 12 months; GenAI adds $2.6–$4.4 trillion globally per year.
- In logistics, GenAI reduces operational costs by 15–30%, boosts delivery efficiency by 25%, and improves forecast accuracy by 35%, yielding a major bottom-line impact.
- Deloitte’s survey confirms smart-manufacturing systems cut defects by ~28%, reduce prototypes by 7%, and trim costs by 29%.
- Healthcare GenAI will save $150 billion per year by 2026; earlier AI tools reduce hospital stays by 17.9%, burnout by 54%, and diagnostic errors by 70%.
You Need To Know:- A Logistics Platform for Automated Parcel Delivery
7. Risks, Governance & Scalability
Traditional AI’s Known Challenges
- Model bias and incomplete data can lead to skewed predictions.
- Focus is narrow—expanding into new tasks requires retraining.
- Integration with legacy infrastructure can be costly.
Generative AI’s Emerging Risks
- “Hallucination”: GenAI might produce incorrect or misleading content.
- Data security: potential exposure of sensitive or proprietary information.
- Environmental impact: AI energy use is rising sharply, already rivaling small countries.
- Regulatory headwinds: Some countries (like China) now mandate AI-generated content labeling.
Common Pitfalls
- High computational and hardware requirements.
- Workforce adaptation challenges—skill gaps in AI integration.
- Ethical implications—especially in healthcare and manufacturing safety.
8. Best Practices for Adoption
- Map your goals: Clarify whether you need precision (Traditional AI), creativity (GenAI), or both.
- Audit data infrastructure: Ensure high-quality, labeled, and secured data.
- Prototype before scaling: Run small pilot projects to test models and workflows.
- Embed governance: Use red-teaming, bias audits, and record logs—especially with GenAI.
- Upskill staff: Train teams to trust and work alongside AI, not fear it.
- Adopt hybrid architectures: Let each AI do what it does best; compose them smartly.
Final Take
Traditional AI delivers reliable, explainable outcomes—perfect for optimization and predictive tasks.
Generative AI brings creative intelligence and customer(dialogue-driven) experiences.
The optimal digital product marries both: apply Traditional AI for internal logic and GenAI to drive UX and adaptability.
With smart layering, logistics systems become efficient and conversational, factories turn static into scenario-powered labs, and healthcare platforms become diagnostic and deeply communicative.
In logistics, smart manufacturing, and healthcare, enterprises are reaping dividends—faster deliveries, safer factories, and better patient outcomes—all backed by multi-billion-dollar cost savings and trillion-dollar economic opportunity.
FAQs
1. What is the difference between Generative AI and Traditional AI?
Traditional AI focuses on tasks like pattern recognition, forecasting, and decision-making—great for logistics and predictive maintenance. Generative AI, on the other hand, creates new content like text, images, or simulations, making it ideal for dynamic user experiences and content generation.
2. Which industries benefit most from Generative AI applications?
Industries like logistics, smart manufacturing, and healthcare are seeing strong ROI from Generative AI. It’s being used for personalized alerts, design simulations, patient summaries, and even new drug development.
3. How does Traditional AI improve operational efficiency in logistics?
Traditional AI streamlines logistics by optimizing delivery routes, predicting disruptions, and managing real-time inventory. It can reduce delivery time by 30%, lower fuel costs by up to 15%, and significantly cut down maintenance expenses.
4. Can Generative AI be used for predictive maintenance in smart manufacturing?
Not directly. Predictive maintenance is typically handled by Traditional AI. However, Generative AI can simulate factory scenarios and optimize equipment layout, which indirectly supports maintenance strategies and boosts efficiency.
5. How does AI reduce downtime in smart factories?
AI-powered systems, especially with IoT integration, predict machine failures and optimize energy use. This leads to 22% less downtime, better production planning, and fewer unplanned outages in manufacturing units.
6. What are the ROI benefits of adopting Generative AI in digital products?
Generative AI pilots often show ROI within 12 months. It helps reduce operational costs by 15–30%, improve delivery accuracy by 35%, and enhance customer satisfaction—all while enabling more responsive, personalized digital products.
7. Is Generative AI safe to use in healthcare applications?
Yes, when implemented with proper guardrails. GenAI is used to draft reports, assist doctors, and support drug discovery. However, it must be closely monitored to prevent errors, protect patient data, and stay compliant with regulations.
8. How can companies blend Traditional AI and Generative AI effectively?
Use Traditional AI for back-end tasks like predictions, diagnostics, and automation. Then, layer Generative AI for customer-facing functions—like chatbots, dynamic content, or scenario modeling. This hybrid model leverages the best of both.
9. What are the risks of using Generative AI in enterprise settings?
Generative AI can produce misleading content, expose sensitive data, and consume large amounts of energy. It also requires careful governance, especially in regulated industries like healthcare and manufacturing.
10. How to choose the right AI model for your digital product?
If your product needs precision, go with Traditional AI. If it needs creativity, personalization, or natural interaction, choose Generative AI. For most modern products, a thoughtful blend of both delivers the strongest performance and user experience.








