The Rise of Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare
The journey of artificial intelligence (AI) in healthcare began with Alan Turing’s 1950 “imitation game,” exploring machine intelligence. However, it was John McCarthy’s 1956 coining of “artificial intelligence” that laid the groundwork for AI’s evolution . Early applications like the 1970s’ MYCIN system attempted to diagnose blood infections but lacked scalability .
The real breakthrough came in the early 2000s with deep learning, revolutionizing fields like radiology and genomics. The COVID-19 pandemic further accelerated AI adoption, from outbreak prediction to telehealth triage.
Market Growth Trajectory
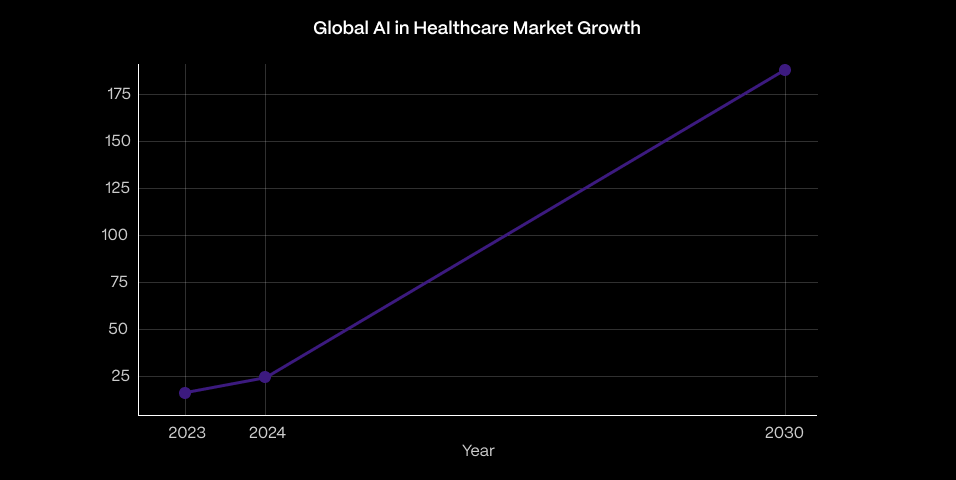
The global AI in healthcare market is experiencing exponential growth:
- 2023: USD 22.45 billion
- 2024: USD 26.57 billion
- 2030: Projected to reach USD 187.7 billion
This represents a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 37.5% from 2024 to 2030.
Regional Market Distribution
AI’s adoption in healthcare varies across regions:
- North America: 57.7%
- Europe: 19.1%
- Asia Pacific: 15.0%
- Latin America: 4.2%
- Middle East & Africa: 4.0%
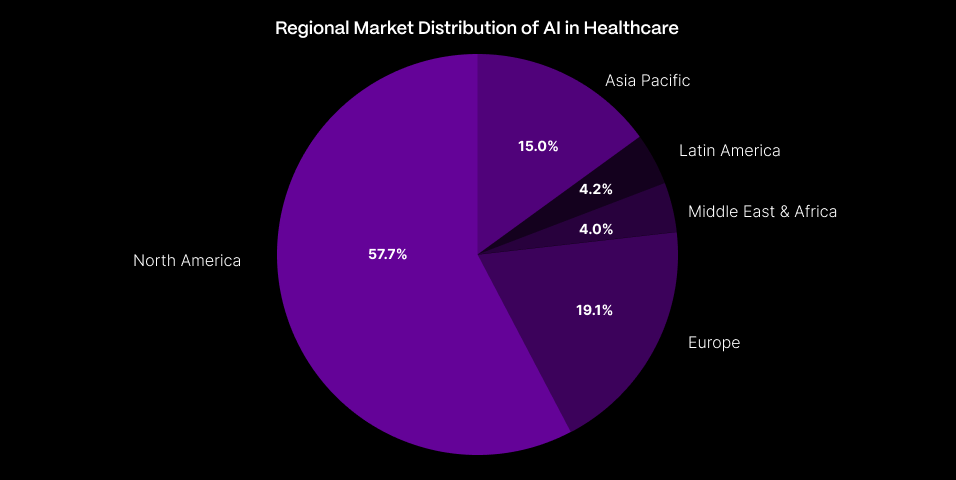
North America’s dominance is attributed to robust digital infrastructure and significant R&D investments, while Asia Pacific’s rapid healthcare market growth indicates potential for increased AI adoption.
The Benefits of Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare
1. Precision Diagnostics
AI enhances diagnostic accuracy and efficiency:
- AI systems detect breast cancer with 99% accuracy, reducing review times.
- As of August 2024, the FDA has authorized 950 AI/ML-enabled medical devices, with a significant focus on imaging and cardiology.
2. Personalized Medicine
Generative AI models analyze tumor DNA to recommend targeted therapies, improving remission rates and minimizing side effects. The generative AI segment is expected to grow at a CAGR of 36.7% through 2030.
3. Operational Efficiency
AI streamlines administrative tasks:
- Tools like Nuance DAX Copilot have doubled investment to USD 800 million in 2024, reducing physicians’ documentation burden.
- Robotic Process Automation (RPA) in claims and billing can cut administrative costs by 20–30%.
4. Enhanced Patient Engagement
AI-powered chatbots and mobile apps improve patient adherence:
- Post-operative monitoring apps increase medication adherence by 40%, halving readmission rates.
5. Accelerated Research & Drug Discovery
AI expedites drug development: In silico screening allows evaluation of millions of compounds in days, reducing R&D costs by up to 30%.
Read Our Case Study:
Streamline Health Management with Smart Device Integration
The Future of Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare
1. Predictive & Preventive Analytics
The next frontier of healthcare will no longer wait for symptoms to appear. With the integration of real-time data from wearable health devices and longitudinal insights from Electronic Health Records (EHRs), AI models can identify subtle physiological changes, well before they escalate into critical events like sepsis, cardiac failure, or diabetic ketoacidosis. This shift from reactive treatment to proactive prevention will transform care delivery models, lower hospitalization rates, and redefine how we monitor chronic and acute conditions. Over time, population-level health trends will be better understood, enabling hyper-personalized wellness strategies and targeted interventions that improve quality of life while optimizing clinical resources.
2. Autonomous & Assistive Robotics
AI-augmented surgical robotics are not just tools—they are co-pilots in precision medicine. Powered by computer vision, real-time data analytics, and machine learning, these systems can execute complex, minimally invasive procedures with accuracy that reduces variability and enhances patient outcomes. From orthopedic surgeries to neuro-navigation, robotics will standardize operating procedures, decrease the risk of human error, and enable shorter recovery times. Beyond the operating room, assistive robots will play critical roles in elder care, rehabilitation, and remote patient assistance, delivering empathetic, consistent, and tireless support to reduce the burden on human caregivers.
3. Generative Clinical Decision Support
AI models like GPT, fine-tuned on medical literature and patient data (with appropriate governance), will act as always-on, context-aware assistants for clinicians. These systems will be capable of generating comprehensive treatment plans, synthesizing differential diagnoses, and mapping care pathways that align with current best practices. By automating clinical documentation, summarizing patient histories, and flagging inconsistencies, these tools will not only reduce administrative fatigue but also improve diagnostic precision. Their ability to serve as real-time consultants will enable clinicians to focus on higher-order decision-making and patient relationships, rather than data interpretation and paperwork.
4. Global Equity & Access
AI holds the power to democratize healthcare by addressing the stark disparities in medical access across geographies. With scalable solutions like AI-driven tele-diagnostics, portable diagnostic devices, and multilingual virtual consultations, patients in rural or underserved regions can access specialist-level insights without needing to travel to urban centers. Low-cost, smartphone-integrated health assessments—ranging from dermatology scans to respiratory analysis—will empower frontline health workers and improve community health outcomes. By decentralizing expertise and reducing cost barriers, AI can be a catalyst for global health equity, particularly in regions where physician-to-patient ratios are critically low.
5. Ethical AI & Governance
As artificial intelligence systems take on greater roles in decision-making and diagnostics, ensuring responsible innovation becomes non-negotiable. Transparent algorithms, regular bias audits, patient consent protocols, and robust data stewardship frameworks must become industry standards. AI must not only perform—it must be explainable, accountable, and equitable. Institutions will need to invest in AI ethics boards, cross-functional oversight, and continuous training of healthcare staff to interpret and question algorithmic recommendations. Trust will be the currency of AI adoption in healthcare, and building that trust will require a delicate balance of technological capability, human oversight, and patient-first governance.
Conclusion
From Turing’s foundational theories to today’s deep-learning applications, AI has transitioned from a conceptual tool to an integral component of healthcare. With the global AI in healthcare market projected to reach USD 187.7 billion by 2030, its influence spans diagnostics, treatment, and operational efficiencies.
Healthcare leaders must embrace AI thoughtfully, ensuring rigorous governance and continuous innovation to fully harness its potential. As we stand on the cusp of this transformation, it’s evident that AI is not just a tool but the stethoscope of the 21st-century physician.
FAQs
1. How is AI used in healthcare?
AI is used across multiple areas of healthcare—from enhancing diagnostics and personalizing treatment plans to streamlining administrative tasks and accelerating drug discovery. Common applications include radiology image analysis, virtual health assistants, remote patient monitoring, and AI-powered surgical robotics.
2. What is the role of AI in healthcare?
AI plays a transformative role in healthcare by improving diagnostic accuracy, enabling predictive care, increasing operational efficiency, and supporting clinical decision-making. It helps healthcare providers deliver faster, safer, and more personalized care at scale.
3. How is AI transforming diagnostics in healthcare?
AI improves diagnostic precision by analyzing medical images, lab results, and patient histories faster than traditional methods. AI tools have shown up to 99% accuracy in detecting breast cancer and are widely used in cardiology, neurology, and pathology.
4. Which regions are leading in AI adoption in healthcare?
North America leads global AI adoption in healthcare with a 57.7% market share, thanks to robust infrastructure and R&D investment. Europe and Asia Pacific are also advancing, with Asia showing rapid growth due to increasing demand and digital transformation.
5. What are the benefits of using AI in healthcare?
AI offers a range of benefits: enhanced diagnostic accuracy, reduced treatment delays, improved patient engagement, lower operational costs, and accelerated drug development. It also reduces the administrative burden on healthcare professionals, improving care quality.
6. How is AI improving personalized medicine?
AI enables personalized medicine by analyzing genomic data, medical histories, and treatment responses to recommend targeted therapies. Generative AI tools can match patients to therapies that are more effective, reducing side effects and improving outcomes.
7. Can AI reduce healthcare costs?
Yes. AI can lower costs by automating repetitive tasks, preventing medical errors, and accelerating research. For example, Robotic Process Automation (RPA) can reduce administrative costs by 20–30%, and AI-driven drug screening cuts R&D timelines significantly.
8. How is AI enhancing patient engagement?
AI-powered apps and chatbots provide 24/7 support, medication reminders, and post-operative care instructions. These tools improve adherence to treatment plans and reduce hospital readmissions by as much as 40%.
9. What are the ethical concerns of AI in healthcare?
Key concerns include data privacy, algorithmic bias, lack of transparency, and accountability. Ethical AI in healthcare requires explainability, patient consent protocols, regular bias audits, and strong governance frameworks to maintain trust and safety.
10. What is the future of AI in healthcare?
AI’s future lies in predictive analytics, autonomous surgical robotics, generative clinical decision support, and global health access. AI will shift healthcare from reactive treatment to proactive prevention, personalizing care while improving system efficiency.