How Technology has Changed Hospital Management
The last decade has witnessed technology change the face of hospital management for improved patient care and operational efficiencies. The practice has become more connected, informed, and patient-centered, with resource management and delivery of care fine-tuned through digital solutions.
According to JMIR publication – From 2015 to 2020, 103,957 remote medical consultations were conducted via the platform, with an annual increasing rate of 0.64%. A total of 86.64% (90,069/103,957) of medical institutions (as clients) that applied for remote consultations were tier 1 or 2 and from less-developed regions; 65.65% (68,243/103,945) of patients who applied for remote consultations were aged over 50 years.
Technical developments, such as AI, smooth the flow of patients, and telemedicine removes time and distance barriers. A report by 2023 shows that over 95% of U.S. hospitals now use certified EHR systems, which afford greater access to patient information and reduce administrative work. 62% would also prefer virtual visits, reflecting the modern trend toward digital healthcare.
Key Statistics Driving Digital Transformation in Hospital Management
- AI for Operational Efficiency: For instance, in the year 2023, AI will be adopted in 59% of hospitals for optimizing patient flow. This will help the hospitals make predictions about admissions, discharges, and transfers to inform decisions and resource utilization.
- Telemedicine’s Growing Popularity: Through all this, telemedicine has just about become a staple of healthcare delivery, pulling 62% of patients who want virtual visits to offer convenience and accessibility not seen previously.
- Widespread EHR Adoption: In 2023, 95% of hospitals in the United States will be ready with adapted certified EHR systems, representing near-universal implementation that improves clinical workflows and patient results.
- Cybersecurity as a Priority: As digital health continues to grow, 59% of healthcare organizations focus on strengthening cybersecurity to protect sensitive patient data and retain the trust of their populations.
- Addressing Workforce Burnout with Automation: With labor shortages and burnout setting in, automation technologies are used by 75% of hospitals to free staff from mundane tasks so they enjoy better job satisfaction and provide better patient care. (World Economic Forum 2023).
By leveraging these cutting-edge technologies, hospitals are improving efficiency, reducing costs, and delivering more personalized and timely care to patients. The impact of technology on hospital management is clear—those who embrace digital transformation are well-positioned to meet future healthcare demands.
Technology plays a leading role in the proper functionality of any hospital today, from administrative operations to clinical procedures. This article pinpoints the changes that technology has brought into hospital management; it focuses on key improved areas both for healthcare providers and patients.
Related Article: Hospital Operations with Workflow Automation
Challenges and Future Prospects
Addressing the Growing Need for Digital Integration
While most of the aspects of technology greatly facilitate the management of hospitals, technology itself posits some particular problems. Installation and maintenance of technological systems are extremely costly; furthermore, the training of personnel is usually quite extensive.
Cyber threats also include patient data leakage; hence, cybersecurity needs updated attention from the principals.
However, the future of hospital management looks bright, especially given emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, blockchain, and robotics that will even further improve efficiency and quality.
AI-driven predictive analytics can help in making informed clinical decisions, while blockchain technology could offer secure ways to store and share patient data.
Related Article: Benefits of AI in Healthcare
Benefits
- Continuous improvement of hospital management systems
- Opportunities for further automation and data analysis
- Better preparedness for healthcare challenges through technological innovation
Key Benefits and Solutions of Technology in Transforming Hospital Management
1. Streamlined Administrative Operations
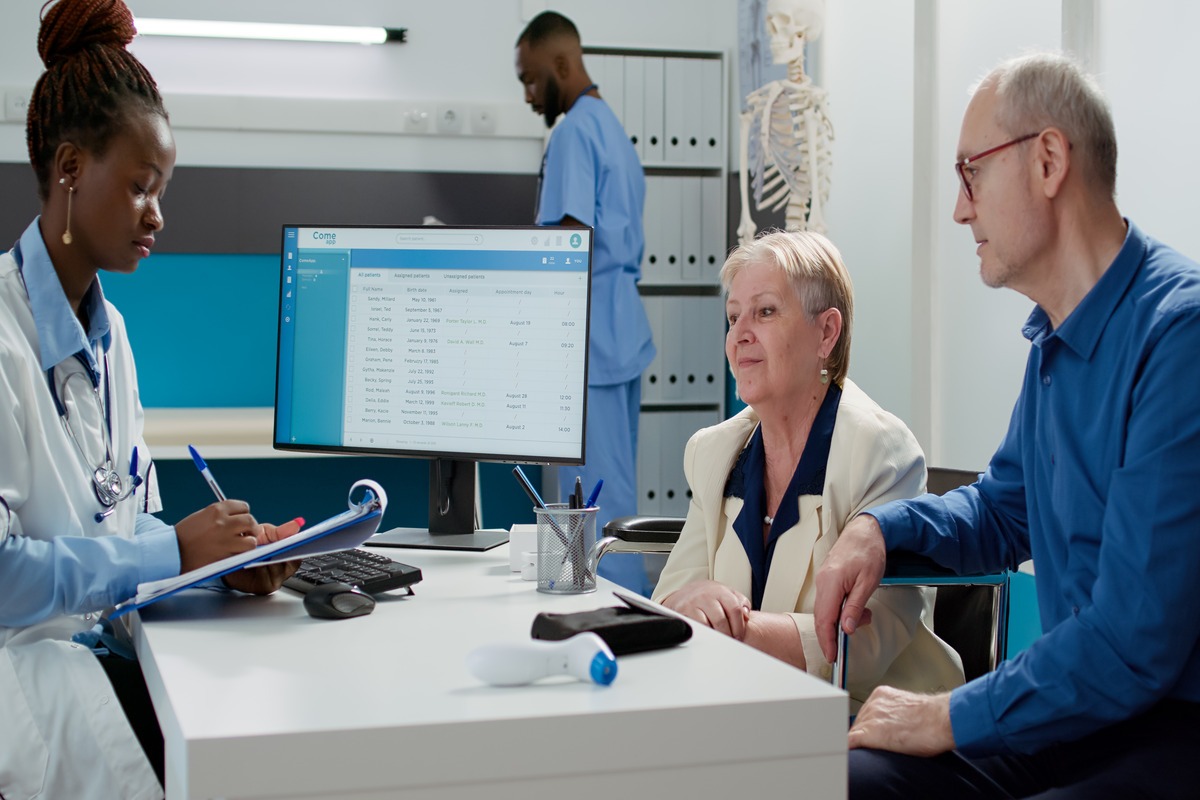

The Backbone of Efficient Hospital Management
For administrative tasks such as handling paperwork, manual scheduling, and high human error risks in hospitals, automation has been incorporated into these with the assistance of technology. The software solutions for this include HMS for simplifying the administrative tasks at the hospital, electronic tools for scheduling, as well as automated billing software. Solutions that not only minimize human errors but also save time for attending personnel for critical tasks.
Other examples include an online appointment booking and management system, which makes it simple for appointments to be scheduled, reducing the waiting time for patients and ensuring that the time of the medical staff is utilized to the fullest.
Besides, automated billing systems ensure that the financial functions are performed with a high degree of accuracy, minimizing errors related to insurance claims and patient billing.
Key Benefits:
- Reduced administrative burden on staff
- Quicker and more accurate patient scheduling
- utomated billing and coding for streamlined financial processes
2. Improved Patient Data Management
Electronic Health Records (EHR) as Game Changers
Perhaps one of the most significant changes brought about by technology is the shift from paper-based records to electronic health records. EHR systems have allowed healthcare practitioners to store, access, and update patient information on a digital platform.
This shift has contributed so much to the management of data in hospitals by facilitating easy access to the correct patient history, test results, and treatment plans.
EHR systems enhance coordination across departments so that all the stakeholders involved in the care of the patients will have current information. The easy access to data reduces the chance of medical errors since the doctors and nurses can go through the patient’s history, medications taken, and past treatments with much speed.
Key Benefits:
- Enhanced accuracy and accessibility of patient data
- Improved patient safety through reduced medical errors
- Easier data sharing across departments for better-coordinated care
3. Enhanced Communication and Collaboration
Breaking Down Silos in Hospital Settings
Efficient communication is the key to optimum hospital management. From secure messaging apps and video conferencing software to integrated hospital management platforms, modern communication tools allow real-time collaboration among healthcare professionals.
For example, interdisciplinary teams can videoconference to discuss complex cases, even if some of the interdisciplinary team members are not on site. With secure messaging, doctors can promptly prompt specialists, which hastens decision-making and helps improve patient care.
With an integrated platform, there is also easy communication among the different heads and breaking down silos that may adversely affect the coordination of effort.
Key Benefits:
- Improved collaboration between departments
- Real-time communication for faster decision-making
- Reduced information silos within the hospital setting
4. Advancements in Patient Care and Monitoring
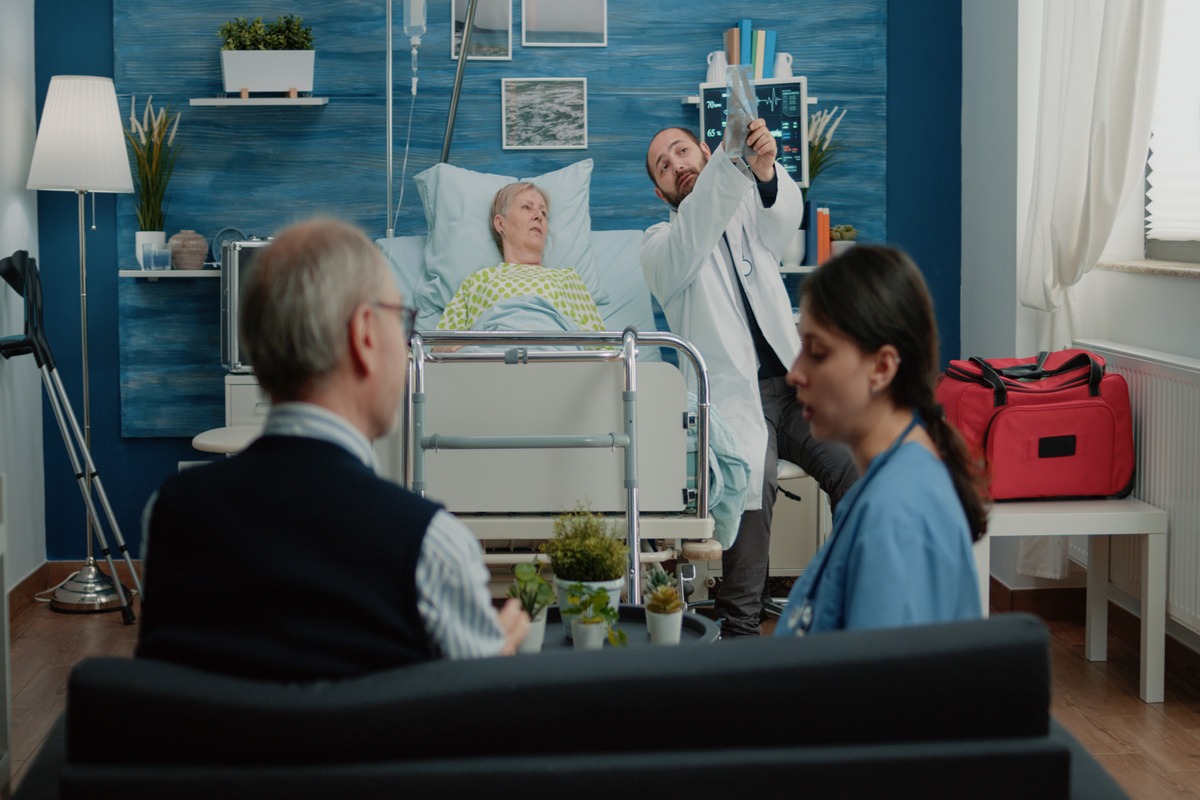

The Role of IoT and Wearables in Patient Health
Care and monitoring have considerably improved at hospitals with the integration of technology. The IoT-coupled medical devices and wearables can measure vital signs in real-time.
Examples include remote monitoring devices, smart infusion pumps, and ventilators that automate ventilation, thereby delivering uninterrupted care without the need for physical checks. Wearables, ranging from heart monitors to glucose sensors and fitness tracker applications, will aggregate data on the patient and automatically send it back to care providers in real-time. This enables proactive health management through the detection of complications well in advance.
Further, smart beds also keep tabs on motion, weight, and vital statistics, thus raising efficiency and quality of care since patients’ monitoring will be possible simultaneously.
Key Benefits:
- Real-time patient monitoring improves proactive care.
- Wearables and connected devices enhance patient autonomy
- Reduced manual tracking by nurses and doctors, leading to more efficient workflows
5. Optimized Supply Chain and Resource Management
Ensuring Efficient Utilization of Resources
A hospital supply chain is very complicated since purchase, storage, and distribution are involved with various medical materials and equipment. Technology-driven inventory management systems help such processes through automation of the supply chain operations.
These systems allow the hospital to track, in real-time, the consumption of all consumables, which enables them to predict and reduce waste and overstocking while ensuring that vital supplies are on hand.
Predictive analytics tools can further project, from the history, trends in patients, and seasonal patterns, the future supplies required for a certain period. This will ensure that at no time do the hospitals get caught off guard by an increased number of patients or demand for resources; this further helps in enhancing efficiency within the operation of hospital facilities.
Key Benefits:
- Improved supply chain efficiency and resource management
- Reduced wastage of medical supplies
- Enhanced preparedness for patient care demands
6. Telemedicine and Remote Care Solutions
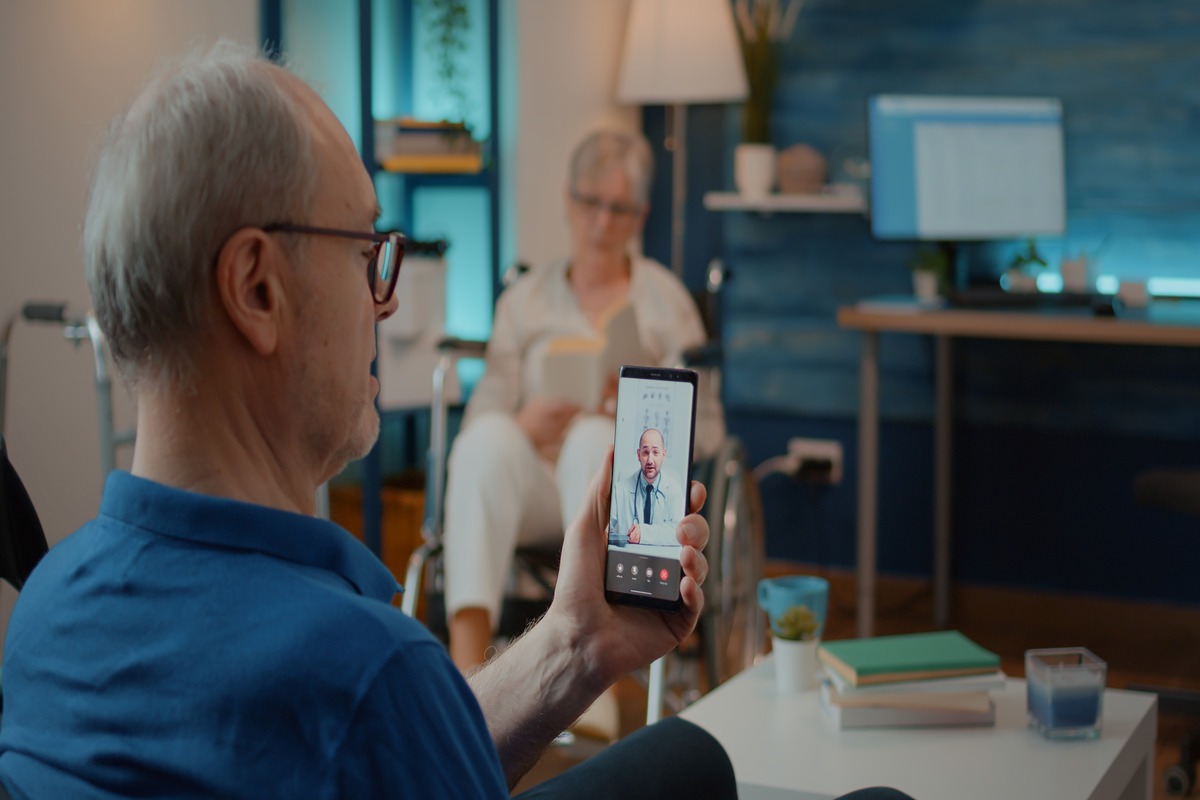

Expanding Access to Healthcare Beyond Hospital Walls
Such revolutionary technology that is involved in hospital management is telemedicine, which increases access to healthcare in both the rural and urban populations.
Telemedicine platforms allow patients to consult doctors from a distance, therefore reducing the need to visit a hospital; hence, chronic conditions are managed with more ease.
This will also help health providers continue to track the health of patients even after discharge through remote monitoring tools.
Applications for telehealth, video consultations, and monitoring of patients remotely make sure that continuous care is provided to those people who cannot visit the hospital frequently due to living in rural areas or having problems with mobility.
Key Benefits:
- Expanded access to healthcare services
- Continuous patient monitoring and support
- Reduced hospital readmissions and in-person visits
7. Enhanced Security and Compliance
Protecting Sensitive Patient Data
The move to digital platforms has necessitated increased security measures to protect sensitive patient data. Hospitals must comply with regulations like the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) to ensure the privacy and security of patient records.
Modern hospital management systems incorporate advanced cybersecurity measures, such as data encryption, access controls, and secure user authentication, to protect patient information from data breaches and unauthorized access. Furthermore, automated compliance tools help hospitals stay up-to-date with regulatory requirements, ensuring that they adhere to legal standards.
Key Benefits:
- Improved data security and privacy
- Simplified compliance with healthcare regulations
- Enhanced trust between patients and healthcare providers
Conclusion
It has come as a paradigm shift in the very concept of hospital management: how all administrative processes, including patient care and communication and even data security, go on. EHR system integration, telemedicine, IoT devices, and advanced security protocols have made the operation of hospitals quick, smooth, and patient-oriented. Though some disadvantages still exist, the advantages far outweigh them, and further technological advancement will only enhance quality and efficiency in hospital management. This means that technology innovation hospitals are more capable of providing quality care, effortless operations, and an overall smooth experience for both patients and caregivers. The future of hospitals is inextricably linked with technological advancement, and nothing but a leading edge can be afforded by healthcare institutions around the world.
FAQs
1. How technology has changed the hospital industry?
The digital transformation in healthcare relates not just to the use of the internet and digital technologies but also does so with new therapies that are being innovated and new best practices being spread out for improved health management procedures. The quality control of huge data collected can help improve patients’ well-being and reduce the cost of services.
2. How is technology used in healthcare management?
It could help in improving efficiency and effectiveness, improving patient experience, and helping doctors by connecting digital systems to make it easier to access information about bed occupancy, device usage, equipment status, material and supply counts, and other operational data.
3. What technology will have the biggest impact on healthcare?
1. Generative AI in Healthcare
2. Personalized Medicine
3. Virtual Healthcare Assistants
4. Digital Twins
5. IoT-Powered Virtual Hospitals and Telemedicine 2.0
6. Preventative Healthcare
7. Virtual and Augmented Reality in Healthcare
8. Elderly Care
4. How has the use of computers and advances in technology changed the healthcare industry?
Computer technology has been carried out in the health care sector, greatly improving access to patient records, efficiency, accuracy, and coordination of care, and resulting in better outcomes for the patients. Its significant use is electronic medical records.
5. What is the role of technology in hospital management?
The technology utilized in caregiving today allows healthcare providers to analyze patient information in ways they may not have been able to before. IT in health enables quality improvement in the delivery of care and improves patient safety through reducing medical errors in addition to enhancing the engagement of the patient and provider.